Sun Safety Factsheets
The 6 topics covered in these factsheets are Sunscreen, Children, Outdoor Sports, and Recreation, Outdoor Workers, Sun Tanning/ Indoor Tanning, and Winter. All are available in English, French, and Arabic.
When exercising, playing, working, or just enjoying time spent in the outdoors, it is important to remember to do it safely. Too much exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation can be harmful by leading to skin/eye damage and even some cancers.
Take measures to protect you and your family from the harmful effects of the sun’s ultraviolet rays.

Cover Up Skin:
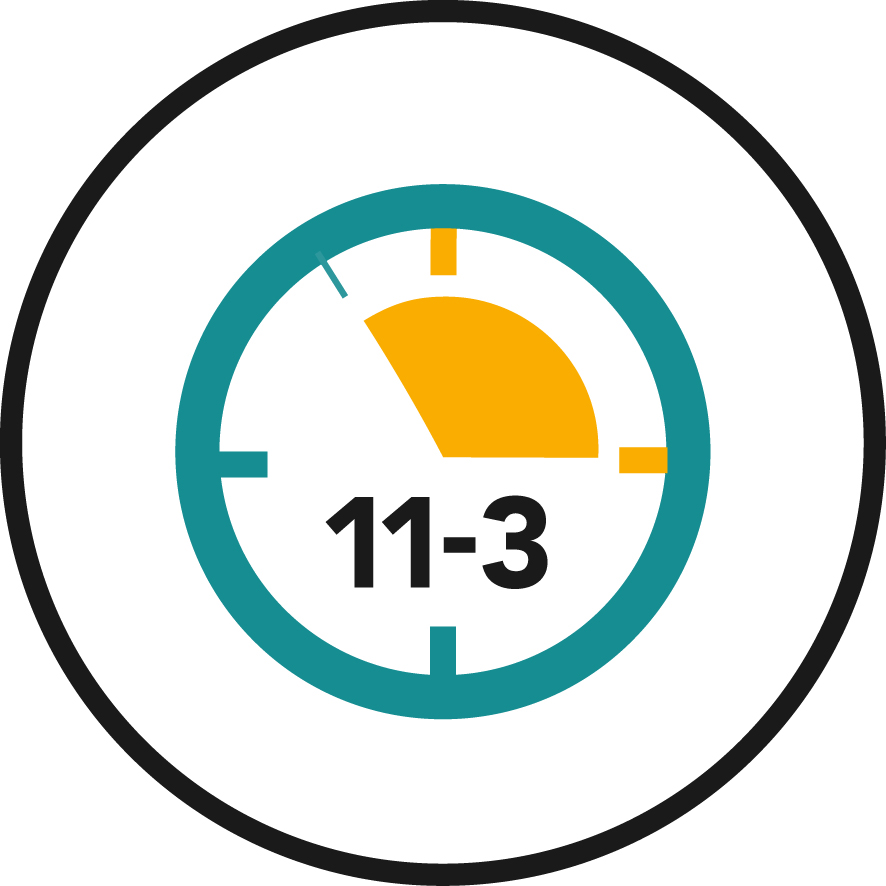
Consider the Time of Day:

Seek Shade:

Apply Sunscreen:

Wear Sunglasses:
For Children:
Consider taking 5 minutes to complete the MyCancerIQ assessment on melanoma by answering Cancer Care Ontario’s questions so that you will receive your own health action plan.
The 6 topics covered in these factsheets are Sunscreen, Children, Outdoor Sports, and Recreation, Outdoor Workers, Sun Tanning/ Indoor Tanning, and Winter. All are available in English, French, and Arabic.
The Ultraviolet Index (UV Index) is a measurement of the intensity of the sun’s rays. The higher the UV index, the more harm done by the sun to your skin, eyes, and immune system.
The best way to protect yourself from damaging ultraviolet (UV) radiation is to cover up, limit your exposure at key times, seek shade, and cover any unprotected areas of the skin with sunscreen.
When your skin is exposed to the sun, it’s able to make vitamin D. Your body needs vitamin D to keep your bones, muscles and teeth healthy. Having the proper amount of Vitamin D is especially important for children and the elderly. However, overexposure to the sun and using a tanning bed increases your chance of developing skin cancer and is not recommended. It is important to develop and maintain good sun protective habits. There are safer ways to maintain healthy Vitamin D levels than through ultraviolet (UV) exposure.
You can get vitamin D from: