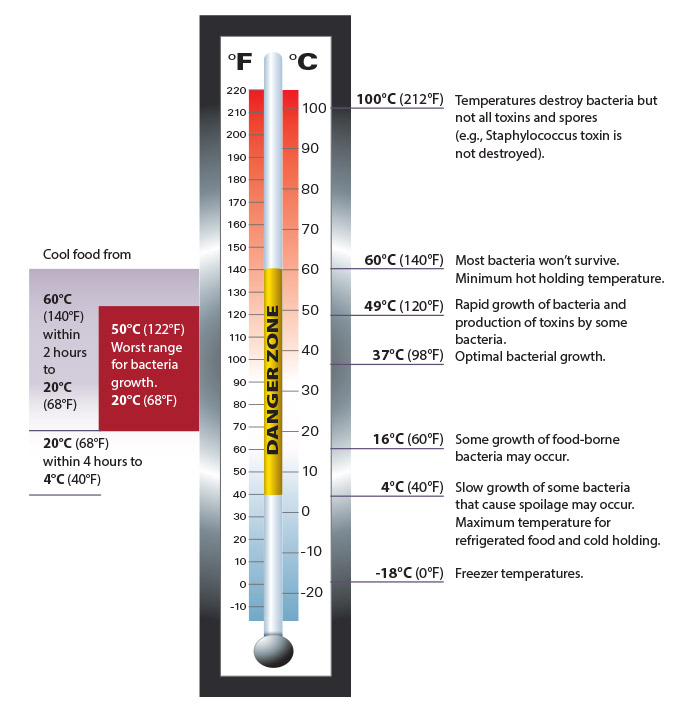
The leading cause of food-borne illness is time and temperature abuse. Temperature abuse of food occurs when food is left at temperatures that are above 4°C (40°F) and below 60°C (140°F). This temperature range is commonly called The Danger Zone. Below are the temperatures you should know.
Download a PDF version of this poster.
Food Temperatures
| Temperature | Description |
|---|---|
| 100°C (212°F) | Temperatures destroy bacteria but not all toxins and spores (e.g., Staphylococcus toxin is not destroyed). |
| 60°C (140°F) | Most bacteria won’t survive. Minimum hot holding temperature. |
| 49°C (120°F) | Rapid growth of bacteria and production of toxins by some bacteria. |
| 37°C (98°F) | Optimal bacterial growth. |
| 16°C (60°F) | Some growth of food-borne bacteria may occur |
| 4°C (40°F) | Slow growth of some bacteria that cause spoilage may occur. Maximum temperature for refrigerated food and cold holding. |
| -18°C (0°F) | Freezer temperatures |
Cooling Food
- Cool food from 60°C (140°F) within 2 hours to 20°C (68°F)
- 50°C (122°F) to 20°C (68°F) is the worst range for bacteria growth.
- Cool food from 20°C (68°F) within 4 hours to 4°C (40°F)

